Options Trading Strategies: A Beginner’s Guide to Profitable Plays
Jeffery ObiagwuShare
What are Options?
Options are financial contracts that give buyers the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a set price within a specific timeframe. They’re used for speculation, hedging, and generating income.
Why Trade Options?
Options offer flexibility, limited risk strategies, and the potential for high returns with less capital. Traders use them to hedge losses, earn income, or speculate on price movements without owning the asset directly.
Basic Options Terminology
- Call Option: Gives the right to buy the asset at a certain price.
- Put Option: Gives the right to sell the asset at a certain price.
- Strike Price: The agreed price for the transaction.
- Expiry Date: The last date the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The cost of the option.
- Intrinsic Value: The real value if exercised now.
- Extrinsic Value: Time and volatility value.
Types of Options Traders
Speculators vs. Hedgers
- Speculators aim to profit from price movements.
- Hedgers use options to protect investments.
Income Seekers
Some investors use options—like covered calls—to earn consistent returns in sideways markets.
Top 7 Beginner-Friendly Options Strategies
- Covered Call: Sell a call on a stock you own to earn income.
- Protective Put: Buy a put to hedge a long stock position.
- Cash-Secured Put: Sell a put on a stock you’d like to own at a lower price.
- Long Call: Buy a call expecting the stock to rise.
- Long Put: Buy a put if you expect the stock to drop.
- Bull Call Spread: Buy one call and sell another at a higher strike.
- Bear Put Spread: Buy a put and sell a lower strike put for bearish markets.
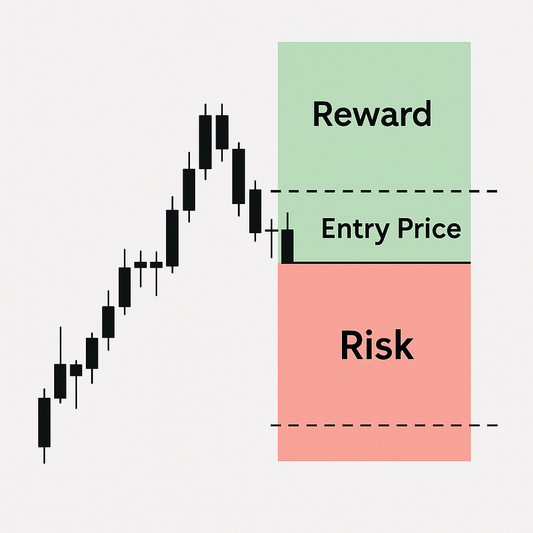
Understanding Risk and Reward
Each strategy has defined:
- Max Gain: The best-case scenario.
- Max Loss: The most you can lose (often just the premium).
- Breakeven Point: Where the profit equals the cost.
Tools and Platforms for Options Trading
Use these to research and trade options:
- Thinkorswim by TD Ameritrade
- Robinhood (Beginner-friendly)
- Options Profit Calculator (Online)
The Greeks Explained Simply
These measure sensitivity to various market conditions:
- Delta: Price change with stock movement.
- Gamma: Delta’s rate of change.
- Theta: Time decay effect.
- Vega: Volatility impact.
Understanding the Greeks helps in choosing the right strategy.
Options Trading Myths Debunked
- “Options are too risky” – Only if misused.
- “Only experts trade options” – Plenty of beginner-friendly strategies exist.
- “You need a lot of money” – You can start with small capital.
Mistakes to Avoid as a Beginner
- Overleveraging: Don’t use too many contracts too soon.
- Holding Till Expiry: Exit before losing premium value.
- Ignoring Volatility: IV directly affects option prices.
When to Use Which Strategy
- Bullish Market: Long call, bull call spread, covered call.
- Bearish Market: Long put, bear put spread.
- Neutral Market: Iron condors, straddles, covered calls.
Understanding Implied Volatility (IV)
IV shows the market’s expectation of volatility:
- High IV = Expensive options
-
Low IV = Cheaper options
Understanding IV helps identify under- or over-priced contracts.
Tax Implications of Options Trading
- Short-Term Gains: Taxed as ordinary income.
- IRS Forms: You’ll need Form 8949 and Schedule D to report trades.
Learning Resources for Options Traders
- Books: “Options Made Easy” by Guy Cohen, “The Options Playbook” by Brian Overby.
- Courses: Options Alpha, TastyTrade tutorials.
- Paper Trading: Use simulators before trading real money.
FAQs on Options Strategies
1. Which strategy is safest?
Covered calls and cash-secured puts are great for beginners.
2. Can I lose more than I invest?
With most beginner strategies, the maximum loss is limited to the premium paid.
3. Are options better than stocks?
They offer more flexibility but are not necessarily “better”—just different tools.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Options trading opens doors to powerful strategies with built-in risk management. Start with simple plays like covered calls or protective puts. Use paper trading to build confidence before going live. Always educate yourself and stay informed—profitable options trading is a marathon, not a sprint.