Risk Management in Trading: Protecting Your Capital Like a Pro
Jeffery ObiagwuShare
Definition and Importance
Risk management in trading refers to the methods and tools traders use to limit potential losses and protect their capital. It’s the backbone of long-term trading success, helping traders stay in the game during inevitable losing streaks.
Why Most Traders Fail Without It
Lack of risk control leads to overexposure, emotional trading, and eventually—account blowouts. Even the best strategy will fail without solid risk management in place.
Types of Risk in Trading
Market Risk
The risk that prices move against your position due to macroeconomic events or news.
Liquidity Risk
Occurs when an asset can’t be sold without affecting its price—common in low-volume stocks or exotic forex pairs.
Leverage Risk
Using borrowed capital amplifies both gains and losses, increasing the chance of margin calls.
Emotional Risk
Trading based on fear or greed can ruin even the best technical setups.
Golden Rules of Risk Management
- Never Risk More Than 1–2% Per Trade: This limits the impact of any single loss.
- Use Stop Losses Religiously: Every trade should have a predetermined exit point.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Avoid concentrating your trades in one asset or sector.
Position Sizing Strategies
Fixed Dollar Amount
Risking a specific dollar amount (e.g., $100 per trade) regardless of account size.
Percentage of Capital
Risking a fixed percentage of your total capital—typically 1–2%.
Volatility-Based Sizing
Using the Average True Range (ATR) to adjust position size based on asset volatility.
Setting Effective Stop Losses
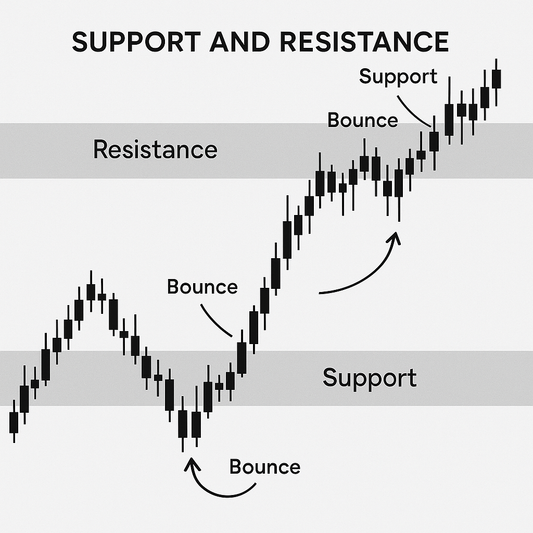
- Percentage-Based Stop: Set at a fixed percent below entry.
- Technical Stop: Placed below support or above resistance levels.
- Time-Based Exit: Exiting after a set period, especially in day trading.
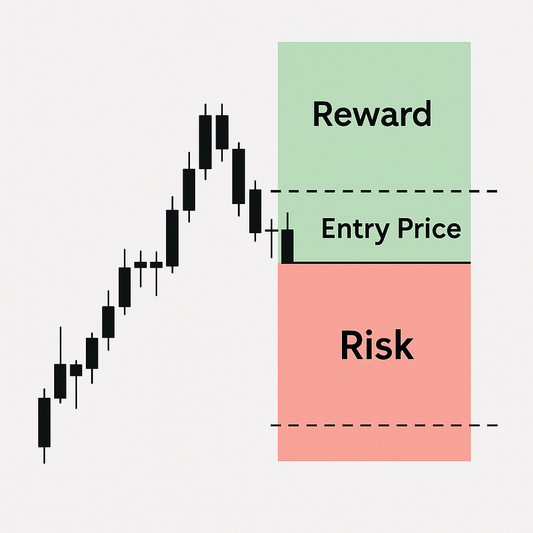
Risk-Reward Ratio Explained
What is Risk-Reward Ratio?
It’s the potential profit versus the potential loss in a trade. A 2:1 ratio means risking $100 to make $200.
Ideal Ratios for Consistent Profitability
Aim for at least 2:1 or better to ensure small wins outweigh occasional losses.
Using Leverage Wisely
- Understanding Margin Calls: Brokers will close your trades if margin drops below requirements.
- The Dangers of Over-Leverage: Amplifies risk and emotional pressure—use it cautiously.
Trade Planning and Pre-Trade Analysis
- Set Entry, Exit, and Stop Before Trading: Prevents emotional decisions mid-trade.
- Use a Trading Journal: Track results, analyze mistakes, and refine strategies.
Psychological Elements of Risk
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Leads to impulsive entries.
- Revenge Trading: Trying to “win back” a loss usually makes it worse.
- Decision Fatigue: Too many trades or choices reduce judgment quality.
Backtesting and Forward Testing Your Strategy
- Simulate Performance: Backtesting helps see how your system would’ve performed in the past.
- Validate Risk Controls: Forward testing in a demo or small live account builds real-time confidence.
Common Risk Management Mistakes
- Ignoring Market Volatility: Don’t use fixed stops in highly volatile markets.
- Adjusting Stops Mid-Trade: Often leads to bigger losses.
- Risking Too Much After a Loss: Leads to emotional overtrading.
How to Recover from a Loss
- Emotional Reset: Step away from the screen if emotions run high.
- Reduce Position Size: Trade smaller until confidence returns.
- Re-Evaluate Your System: Review what went wrong and adjust.
Using Technology for Risk Management
- Trade Management Tools: Automate exits and position sizing.
- Mobile Alerts: Get notified if price hits key levels.
- Automation: Use bots or scripts to enforce your risk rules.
FAQs on Trading Risk Management
1. What’s the safest position size?
Typically 1–2% of total capital per trade.
2. Should I always use stop-loss orders?
Yes. They’re essential to managing risk, especially in volatile markets.
3. How can I measure risk effectively?
Use position size calculators and track historical volatility (e.g., ATR).
Conclusion and Action Plan
Risk management isn’t optional—it’s essential. Focus first on preserving capital before trying to grow it. Stick to your plan, keep your emotions in check, and constantly improve your process. Remember, in trading, surviving is winning.